
Complete Smell & TasteTM
90 Capsules $32.98
90 Capsules $32.98
Most people like the smell and taste of food. However, many people, especially as they age, begin to lose some of their senses of smell and taste. “Over 2 million people in the United States have disorders of taste and smell” [1]. Many also have complaints such as dry mouth.
Since most who do begin to lose these senses presume that it is simply age-related, they normally do nothing about it and let the deterioration continue. Some complain of losing their appetite and any interest in cooking. A loss of senses can be frustrating because they affect a person’s ability to enjoy food, drink, aromas, and often life itself. Weight loss, sometimes excessive loss, often accompanies loss of taste and smell [2].
Smell and taste are closely linked with both sensations being transmitted to the brain which then combines the two lots of information to correctly recognize and appreciate flavors. Many of the more complex flavors require both taste and smell to be properly sensed.
A loss of the sense of smell is called anosmia while limited loss is termed hyposmia [3]. Smelling disorders occur more frequently than taste loss. While there are innumerable smells, they have been classified into the categories of camphoraceous, musky, floral, pepperminty, ethereal, pungent, and putrid [4]. Some people have odor blindness which means that they cannot detect the smell of single substances—discrete odor blindness has been identified in over 50 substances [4].
The sense of smell is complex. It can be affected by changes in the nose, mucous, liver problems, the nerves leading from the nose to the brain, or simply in the brain. In addition to age, allergic rhinitis, head trauma, depression, low estrogen, upper respiratory infections, or chronic nasal infections are often implicated [2-6].
The loss of the sense of taste is called ageusia, while an impairment of taste is called hypogeusia. Although there are at least thirteen possible taste receptors [4], tastes that the tongue detects include sweet, sour, salt, pungent (hot spicy), bitter, and glutamate. Loss of taste is normally caused by conditions that affect the tongue such as dry mouth, certain medications, depression, smoking, or radiation therapies [2-5].
In addition to loss of enjoyment in eating, loss of taste and smell can be potentially dangerous as they warn us about items that have gone bad that we should not eat, dangerous chemical odors, and can even have an effect on matters such as libido. What if there are nutritional deficiencies that contribute to this loss? Would not nutritional supplementation be preferable to losing ones’ smell and taste senses?
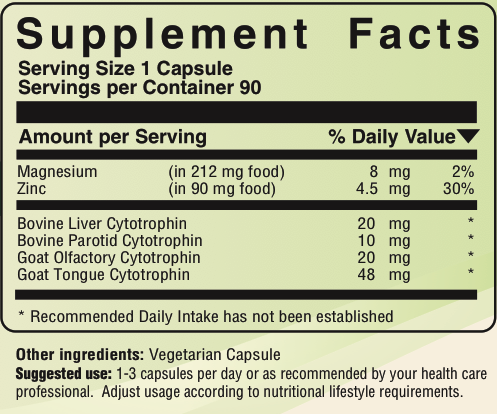
Complete Smell and Taste contains the following Foods:
Bovine Liver. It has been reported that “Acute and chronic liver disease can effect taste, smell, food preference and appetite” [6]. The liver is the chemical factory of the body and makes many enzymes that affect essentially every function in the body. One study found that 71% of those with liver cirrhosis had impairment to their ability to smell [7].
Bovine Parotid. Parotid glands are a type of salivary glands (there are other salivary glands in the tongue). Bovine parotid glands have been advised for “Salivary disorders…Diminished salivation, enlargement of the salivary glands…Mouth-tongue disorders” [8]. In other words, parotid has long been advised for people with dry mouths.
Goat Olfactory Tissue supplies peptides, enzymes, and other components found in the olfactory components of the nasal cavity. “Each olfactory sensory neuron in the olfactory epithelium expresses a single type of odorant receptor that binds odorants on the basis of their molecular features. Different types of receptors are expressed in different parts of the nose, some in separate organs, or in different compartments or zones of the main olfactory epithelium. In the main epithelium, most odorant receptor expression zones may be functional anatomical units, because they are organized orthogonally to airflow, establishing an interaction between chromatographic separation of odorants across the nasal mucosa and receptor specificity to establish the unique activity patterns across the epithelium that are evoked by different odorant molecules.
There are specialized peripheral organs in the nose that project to separate small sets of olfactory bulb glomeruli, while the zones of the olfactory epithelium project to corresponding zones within the glomerular layer of the bulb inner ear such as the inner ear hair cells” [9]. Proponents of glandular therapies believe that ingestion helps the corresponding organ in humans [10].
Goat Tongue, low temperature dried. The taste buds are located in the tongue [4]. Low temperature dried goat tongue naturally contains all the peptides, enzymes, sensory glands, salivary glands, and other substances found in tongues. Tongue tissue also naturally contains small quantities of essential nutrients such as zinc, niacin, and magnesium [11].
Magnesium One study found that oral magnesium consumption reported that 71% demonstrated increased smell function on testing [12]. A taste study involving liver patients found that serum “magnesium was significantly negatively associated with detection of salt (P = .02) and gustatory score (P = .02)” [13].
Rice is a natural Food source of B vitamins. Specifically, rice naturally contains vitamins B-1, B-2, B-3, B-5, B-6, and B-8, plus minerals [14]. B complex vitamins are needed for tongue health [15].
Zinc is an essential mineral that improves the senses of smell and taste. One study found involving zinc supplementation concluded that its data supported the view that gustin/carbonic anhydrase VI is a trophic factor that enhances growth and development of taste buds by acting on the taste bud stem cells [16]. Notice that, “[a]lthough the specific role of zinc in the control of taste or smell is unknown, it is functionally involved at several levels of cellular organization. At the receptor level, in the taste bud, zinc is a cofactor in alkaline phosphatase, the most abundant enzyme isolated from the taste bud membrane. The cells of the taste buds are provided with microvilli in direct communication with the oral cavity through an apical pore. A protein (gate-keeper) regulates the diameter and permeability of the pore and its membrane, which in turn control the quality of stimuli that pass through the pore per unit of time. Conformational changes in these protein molecules are controlled by the equilibrium of metals and, consequently, a deficiency of some metals, zinc in particular, is reported to be associated with hypogeusia” [17]. “Zinc deficiency is common in the elderly and defined as a plasma level less than 15 umol/l. The mean intake in the elderly between 50 and 80 years of age has been reported to be 9.06 mg per day which is 69% of the recommended daily allowance. Zinc appears to be effective in taste disorders only with low zinc concentrations. Elemental zinc supplementation in daily doses of 25 to 100 mg per day by mouth appears to be beneficial in taste disorders secondary to zinc depletion" [1].
The senses of smell and taste are important. Complete Smell and Tatse is the only mineral-claiming 100% Food supplement we are aware of intended to nutritionally support these senses.
Nutrition from food, what a concept!
References
[1] Heyneman, CA. Zinc Deficiency and Taste Disorders. Ann Pharmacotherapy, 1996;30:186-187
[2] Vissink A, van Weissenbruch R, van Nieuw Amerongen A.
Disorders of taste and smell. Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd.
2001;108(6):229-236
[3] Henkin RI. Drug-induced taste and smell disorders. Incidence,
mechanisms and management related primarily to treatment of sensory
receptor dysfunction. Drug Saf. 1994;11(5):318-377
[4] Guyton AC, Hall JE. Textbook of Medical Physiology, 9th ed. W.B. Saunders Co, Phil., 1996
[5] Deems DA, Doty RL, Settle RG, Moore-Gillon V, Shaman P, Mester AF,
Kimmelman CP, Brightman VJ, Snow JB. Smell and taste disorders, a
study of 750 patients from the University of Pennsylvania Smell and
Taste Center. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
1991;117(5):519-528
[6] Hamilton K, et al. Clinical Pearls 1994. ITServices, Sacramento, 1994
[7] Temmel AF, et a1. Dysfunction of the liver affects the sense of smell. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2005;117(1-2):26-30
[8] Lee R. Parotid Cytotrophin. Lee Foundation for Nutritional Research, Milwaukee, circa 1950
[9] Leon M, Johnson B. Functional units in the olfactory system. PNAS, 2006; vol. 103, no. 41:14985-14986
[10] Thiel R., Fowkes S.W. Down syndrome and thyroid dysfunction:
Should nutritional support be the first-line treatment? E-pub
March, 2007
[11] Lamb, variety meats and by-products, tongue, raw. USDA Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 19, 2006.
[12] Henkin, R.I., Nelson, N.R.Changes in Smell Function in Patients
With Hyposmia After Magnesium Treatment", J Am Coll Nutr, 1991;10(5):548
[13] Madden AM, Bradbury W, Morgan MY. Taste perception in
cirrhosis: its relationship to circulating micronutrients and food
preferences. Hepatology. 1997;26(1):40-8.
[14] Rice bran, crude. USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 17, 2004
[15] Shils M, et al eds. Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease,
10th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Phil., 2006
[16] Henkin RI, Martin BM, Agarwal RP. Efficacy of exogenous oral zinc
in treatment of patients with carbonic anhydrase VI deficiency. Am J
Med Sc, 1999;318(6):392-404
[17] Hamilton K, et al. Clinical Pearls 1998 with the Experts Speak. ITServices, Sacramento, 1998, p.42
Some of these studies (or citations) may not conform to peer review standards, therefore, the results are not conclusive. Professionals can, and often do, come to different conclusions when reviewing scientific data. None of these statements have been reviewed by the FDA. All products distributed by Doctors’ Research, Inc. are nutritional and are not intended for the treatment or prevention of any medical condition.
 |
||
|
||