
GB Support TM
90 Capsules $26.98
90 Capsules $26.98
Some people who have been told they have irritable bowel syndrome have gallbladder or other problems [1]. People who have biliary stasis, gallstones, or have had their gallbladders removed often suffer from painful bouts of indigestion. Many who have found that the more common approaches to constipation are ineffective, may have a diagnosed or undiagnosed problem with bile flow or have gallstones. “Chronic cholecystitis and gallstones predispose to cancer of the gallbladder” [2]. It is also reported that some gallbladder problems can predispose some to acquire a variety of mycotic infections, such as aspergillus or rhizipus species [3]. A properly functioning gall bladder is essential for proper digestion and helps prevent gallstones [4].
In a very real sense, the gallbladder functions as part of a natural recycling system. Bile, which it expels after being stimulated by cholecystokinin in the presence of fat, is actually composed of cholesterol and used up red blood cells [4]. This is one of the reasons that cholesterol can rise if the gallbladder is not properly functioning. “Only about 20% of people who have gallstones get symptoms…A major sympton of gallstones is usually a right-sided pain in the abdomen that may be associated with shoulder pain. The shoulder pain may occur by itself without the abdominal pain. There may be centrally located upper abdominal pain over the breastbone. The pain in general, where it manifests, is constant and progresses slowly, rising to a plateau, and then gradually decreases, usually within several hours after a meal, especially after meals containing large amounts of fat. If the abdomen gets extremely painful, even to the touch, this may be a symptom of acute cholecystitis. This is irritation and infection in the gallbladder usually do to a gallstone being trapped” [5]. On the other hand, some with mild biliary stasis often experience sharp pains, nearly anywhere in the abdomen. While others experience little, if any, pain, but tend towards constipation.
Many people’s digestive systems can benefit from 100% Food GB Support.
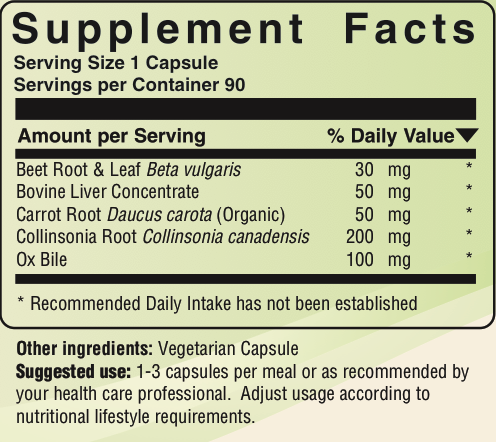
Beet leaf and root provide fiber andhave long been used in combination with carrots to help in conditions of “liver and gallbladder stasis” [6]. Beet leaf and root is “used as supportive therapy in diseases of the liver and fatty liver” [7]. It is believed that this is probably due to the fact that beet contains betaine [7]. Betaine is a metabolite of choline [8]. “Beets have been known to aid in lymphatic function and to stimulate gall bladder and liver function. This is especially important when detoxifying the body, as these organs are the primary avenues of detoxification” [9]. “Beets and beet juice have also been used to eradicate gallstones, kidney stones, bladder disorders, and kidney disease” [10].
Bovine Liver supplies liver tissue. “Bile is secreted in two stages by the liver: (1) the initial portion is secreted by the liver hepatocytes ; this initial secretion contains large amounts of bile acids, cholestrol, and other organic constituents. It is secreted into minute bile canaliculi that lie between the hepatic cells in the hepatic plates. (2) Next, the bile flows peripherally toward the interloba septa, where the canaliculi empty into terminal bile ducts and then into progressively larger ducts, finally reaching the hepatic duct and common bile duct, from which the bile either empties directly into the duodenum or is diverted through the cystic duct into the gallbladder” [4]. The liver tissue in GB Support is from New Zealand.
Carrots have long been used in combination with beet leaf to help in conditions of “liver and gallbladder stasis [6]. “Scientists in India have discovered that carrots afford significant protection for the liver” as carrots contain substances which “increase the activity of several enzymes that speed up detoxification of the liver and other organs” [11]. “Scottish studies showed that over a period of three weeks, a daily snack of two carrots lowered cholesterol levels by 10 to 20 percent in study participants. Carrots are high in the fiber pectin” [11].
Collinsonia Root is also called stone root and has tonic effects [8]. It is most often used for stomach complaints, hemorrhoids, or constipation [9,12], while its tonic effects within the bowels help maintain a state of calm (and also helps the bowels function more naturally). It is “[o]f reputed value in Varicose Vein conditions and for Hemorrhoids” [13]. It has long been used in combination with ox bile to help support bile flow and deal with indigestion [14]. Collinsonia root “is used for calculi, kidney stones, urea (bladder semolina), bladder inflammation, dropsy and gastrointestinal disorders” [8].
Ox bile is a source of bile. It has been written that oral consumption of bile salts, “a. Stimulates bile flow b. Combats constipation c. Promotes absorption of fat and fat-soluble vitamins” [14 ] “One of the many functions of the liver is to secrete bile, normally between 600 and 1200 ml/day. Bile serves two important functions: First, it plays an important role in fat digestion and absorption, not because of any enzymes in the bile that cause fat digestion, but because of bile acids in the bile that do two things: (1) they help emulsify the large fat particles of the food into many minute particles that can be attacked by the lipase enzyme secreted in pancreatic juice and (2) they aid in the transport and absorption of the digested fat end products to and through the intestinal mucosal membrane. Second, bile serves as a means for excretion of several important waste products from the blood. These include especially bilirubin, an end product of hemoglobin destruction, and excesses of cholesterol…The bile secreted by the liver is normally stored in the gallbladder until needed in the duodenum” [4].
One study concluded, “Although fat malabsorption in the short-bowel syndrome is caused in part by decreased bile acid secretion, bile acid replacement therapy is not used because of the belief that ingested bile acids would worsen diarrhea, outweighing the benefits of improved fat absorption… This study compared the effect of a natural conjugated bile acid mixture from ox bile…In balance studies, conjugated bile acid replacement therapy…caused fat absorption to increase by approximately 40 g/day. Calcium absorption also increased. Neither bile acid product caused a clinically significant increase in ileostomy water output…Conjugated bile acid replacement therapy should be part of the armamentarium for the treatment of selected patients with the short-bowel syndrome” [15].
Although bile is sometimes advised when gallbladder problems (including gallstones) are present, “bile is contraindicated if ulcers co-exist” [5] and may not be agreeable for some with biliary stasis [14] or sometimes diarrhea. The ox bile in GB Support is from New Zealand.
Products containing ox bile, collinsonia, carrots, bovine liver, beet leaf, and/or beet root have long been recommended for those with ‘venous congestion of the liver’ or gallstones [e.g. 13,14,16-18] or even certain mycotic (yeast) infections [3].
Food supplements, actually made of Food, are superior and more natural than those filled with isolates!
Many people simply take GB-Support as a Food supplement to help them feel better.
Unlike many so-called “natural” formulas, GB Support is only comprised of foods, contains no synthetic USP nutrients or isolated mineral salts, but only contains foods, food complexes, and food concentrates.
Numerous university studies have concluded that supplements containing food nutrients are better than USP isolates. Food nutrients are better because they contain important enzymes, peptides, and phytonutrients CRITICAL to the UTILIZATION of vitamins and minerals which are not present in isolated USP nutrients. Published research has concluded that food vitamins are superior synthetic/USP vitamins.
Suggested use: 1-3 capsules per meal or as recommended by your health care professional. Adjust usage according to nutritional lifestyle requirements.
References
[1] Adeniji OA, Barnett CB, Di Palma JA. Durability of the diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome based on clinical criteria. Dig Dis Sci. 2004 Apr;49(4):572-574
[2] Thun MJ, Henley SJ, Gansler T. Inflammation and cancer: an epidemiological perspective. Novartis Found Symp. 2004;256:6-21; discussion 22-8, 49-52, 266-269
[3] Thiel R. Systemic mycoses: An overview for natural health professionals. Orig Intern. 2002;9(4):42-51
[4] Guyton AG, Hall JE. Textbook of Medical Physiology, 9th ed. W.B. Saunders Co., Phil., 1996
[5] Strohecker J, sr. editor. Alternative Medicine: The Definitive Guide. Future Medicine Publishing, Inc., Fife (WA), 1995
[6] Lee R. Vitamins A & F With Betafood. In Product Bulletins, circa 1950
[7] Beers MH and Berkow R, eds. The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy, 17 th ed. Merck Research Laboratories, Whitehouse Station (NJ), 1999
[8] Gruenwald J, Brendler T, Jaenicke C, eds. PDR for Herbal Medicine, 2nd ed. Medical Economics, Montvale (NJ), 2000
[9] Cotran RS, Kumar V, Collins T. Robbins Pathologoical Basis for Disease, 6 th ed. WB Saunders, Phil, 1999
[10] Ingram C. Super-Market Remedies. Knowledge House, Buffalo Grove (IL), 1998
[11] Duke JA. The Green Pharmacy. Rodale Press, Emmaus (PA), 1997
[12] Scalzo R. Naturopathic Handbook of Herbal Formulas, 3 rd ed. Kivaki Press, Durango (CO), 1994
[13] Lee R. Collinsonia. In Product Bulletins, circa 1950
[14] Lee R. Cholacol. In Product Bulletins, circa 1950
[15] Gruy-Kapral C, Little KH, Fordtran JS, Meziere TL, Hagey LR, Hofmann AF. Conjugated bile acid replacement therapy for short-bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1999 Jan;116(1):15-21).
[16] Harrower H. An Endocrine Handbook. The Harrower Laboratory, Glendale (CA), 1939
[17] Versandall DA. Contact Reflex Analysis and Applied Trophology. Dr. D.A. Versendaal, Holland (MI), 1990
[18] Lee R. Gall Bladder Dysfunction. In Therapeutic Food Manual, circa 1950
Some of these studies (or citations) may not conform to peer review standards, therefore, the results are not conclusive. Professionals can, and often do, come to different conclusions when reviewing scientific data. None of these statements have been reviewed by the FDA. All products distributed by Doctors’ Research, Inc. are nutritional and are not intended for the treatment or prevention of any medical condition.
 |
||
|
||
