
Complete Ear HealthTM
90 Capsules $32.98
90 Capsules $32.98
Hearing problems are exceptionally common. From tinnitus to actually hearing loss, there are numerous hearing problems. Actually “disorders of the auditory system affect nearly 28 million Americans” [1], with over 23.2 million having hearing loss [2]. “Doctors divide hearing loss into two basic categories: conductive hearing loss, which occurs when the passage of sound waves is impeded in the external and middle ear, and sensorineural hearing loss which results from damage to the structures or pathways of the inner ear” [2].
Tinnitus is characterized by a continuous ringing or hissing in the ear, sometimes accompanied by pain. Causes can include excess ear wax, a blocked eustachian tube, and a dysfunction of the auditory nerve [1]. Allergies may also play a role. If the problem is heart or brain caused, non-nutritional treatment should be sought. “Acute otis media is characterized by an infection in the middle ear (usually bacterial) and is often accompanied by an upper respiratory infection…Chronic otis media…refers to a constant swelling and blockage of the auditory tube” [1].
“Sensory hearing loss in adults is a common occurrence, usually resulting from the loss of hair cells in the inner ear responsible for transmitting sounds to the nerves”. According to Dr. C. Kotsanis, “Many disorders of the ear can be traced to infection, loud noise, and a variety of food and environmental allergies [1].
According to the League for the Hard of Hearing , “Hearing aids…do not restore normal hearing. Despite what some manufacturers of hearing devices may advertise, hearing aids do not cure hearing loss [3]. According to the National Institute on Aging hearing aids make “sounds louder” [4]--it makes one wonder if hearing aids, especially if improperly fitted, may possibly contribute to further hearing loss [3].
Although often ignored by many in the mainstream, scientific research confirms that there are nutrients in foods that can help provide support for ear health.
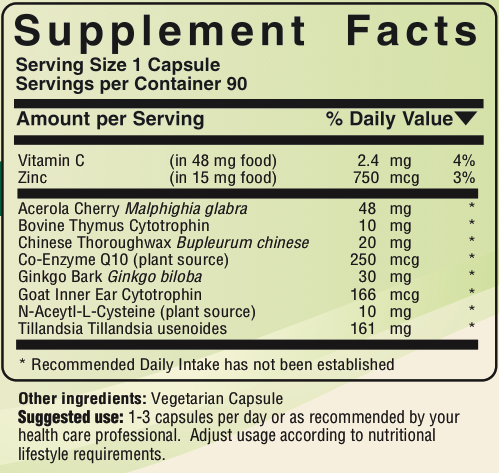
Complete Ear Health contains the following Foods:
Acerola cherry, Malphighia glabra, “is one of the riches sources of vitamin C in the world…Acerola also contains flavonoids, other vitamins, such as thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, panto…and beta carotene, and minerals, such as magnesium and potassium” [5]. Vitamin C with bioflavonoids has been advised “to aid in the preventing of ear infections” [4].
Bovine Thymus. It has been reported that “thymus extract giving orally has been shown to decrease children’s food allergies, improve immune function, and may be of particular benefit in otis media” [1]. It naturally contains nutrients such as manganese, potassium, and zinc [6], which have sometimes been recommended for better hearing [2].
Chinese Thoroughwax, also called Chai-Hu or Bupleurum chinense, has traditionally been used in China for problems including deafness [7]. It contains various saikosaponins, including saikosaponin 1, which has been found to reduce ear edema in a mouse study [8].
Co-Enzyme Q10 may prevent hearing loss according to animal and human studies. It also might be able to reverse some loss of inner ear hair cells [9]. One human study found that it may delay the progression of hearing loss [10]. Also, “it has been reported that CoQ10 is effective in promoting recovery from acute sudden deafness” [9]. CoQ10 and vitamin B-6 together seem to improve immune response [11].
Folate One study found“supplementation slowed the decline in hearing of the speech frequencies associated with aging in a population from a country without folic acid fortification of food” [12].
FOOD RESEARCH PRODUCTS ARE 100% FOOD!
Gingko Biloba “Ginkgo biloba is commonly used in the treatment of…tinnitus of vascular origin” [13]. A French randomized, placebo-controlled trial of 103 patients showed 50 percent of patients with new-onset tinnitus had improvement or disappearance of symptoms in 70 days compared with 119 days to improvement in those receiving placebo.study [14], yet other research has not duplicated these results, though those positive ones have tended to have higher dosages like 120-160 mg per day [5].
Goat Inner Ear Tissue supplies peptides, enzymes, and other components found in the inner ear such as the inner ear hair cells. “Sensorineural hearing loss may result…from damage to tiny cells called hair cells in the inner ear. The hair cells are responsible for translating sound waves into nerve impulses for transmission to the brain” [2]. Proponents of glandular therapies believe that ingestion helps the corresponding organ in humans [15].
N-Aceytl-L-Cysteine Dr. K. Data recommends the use of n-aceytl cysteine to remove fluid associated with chronic otis media [1]. One study reported, “It has been shown that antioxidants such as N-L-acetylcysteine (NAC) can protect the inner ear from oxidative damage” [16]. It has been recommended to “remove excess fluids from the ear canal” [2].
Rice is a natural Food source of B vitamins. Specifically, rice naturally contains vitamins B-1, B-2, B-3, B-5, B-6, and B-8, plus minerals [17]. B complex vitamins are sometimes recommended for ear health [2].
Tillandsia is an epiphytic plant which is a member of the bromeliaceous family. Although it grows on other plants, it is not a parasite. It derives its nutrients from the air, sunlight, and rain. It has strong absorbtive properties. It seems to have an affinity for ear canals as well as the ability to remove some unwanted substances from that area. Since sometime in the 20th century, the combination of tillandsia and B vitamins have been used for hearing related issues [18,19].
Vitamin B6 is associated with nerves. Deficiency of vitamin B6 apparently can reduce the ability to respond to sounds [20]. Vitamin B6, along with vitamins C and B12 and other substances, have been used together to reverse “sudden deafness” [21].
Vitamin B12 A human study suggested “a relationship between vitamin B12 deficiency and dysfunction of the auditory pathway. Some improvement in tinnitus and associated complaints were observed in 12 patients following vitamin B12 replacement therapy” [22]. Vitamin B12 deficiency appears to be correlated to noise-related hearing loss [23]. Another study concluded that B12 “levels may reduce the risk of hearing dysfunction resulting from noise exposure in healthy, young subjects” [23]. Elderly people often have low B12 levels [5].
Zinc is located in the inner ear as the cochlea has the body's greatest concentration of it [25]. An animal study found that a zinc injection prevented salicylate-induced hearing loss [26]. A human study concluded, “that patients with tinnitus may have low blood zinc levels (31%) and clinical and subjective improvement can be achieved by oral zinc medication” [27]. Another human study concluded, “zinc is involved in the generation of tinnitus, especially in patients whose hearing is relatively normal” [28].
Your hearing is important. Complete Ear Health is the only mineral containing 100% Food supplement we are aware of intended to nutritionally support the ears.
Nutrition from food, what a concept!
References
[1] Strohecker J, ed. Alternative Medicine, The Definitive
Guide. Future Medicine Publishing, Fife (WA), 1995
[2] Balch JF, Balch PA. Prescription for a Nutritional Healing,
2nd ed. Avery Publishing, Garden City Park (NJ), 1997
[3] League for the Hard of Hearing. website
[4] Age Page. Hearing Loss. National Institute on Aging, U. S.
Department of Health and Human Services.
http://www.niapublications.org/agepages/hearing.asp
[5] Sheldon S, Rorvik D, eds. PDR for Nutritional Supplements. Medical Economics, Montvale (NJ), 2001
[6] Beef, variety meats and by-products, thymus raw. USDA
National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 19, 2006
[7] Gruenwald J, Brendler T, Jaenicke C, eds. PDR for Herbal Medicine, 3rd ed. Thomson PDR, Montvale (NJ), 2004
[8] Bermejo Benito P, Abad Martinez MJ, Silvan Sen AM, Sanz Gomez A,
Fernandez Matellano L, Sanchez Contreras S, Diaz Lanza AM. In
vivo and in vitro antiinflammatory activity of saikosaponins.
Life Sci. 1998;63(13):1147-1156
[9] Sato K. Pharmacokinetics of coenzyme Q10 in recovery of acute
sensorineural hearing loss due to hypoxia. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl.
1988;458:95-102
[10] Angeli SI, Liu XZ, Yan D, Balkany T, Telischi F. Coenzyme
Q-10 treatment of patients with a 7445A--->G mitochondrial DNA
mutation stops the progression of hearing loss. Acta Otolaryngol.
2005 May;125(5):510-512
[11] Folkers K, Morita M, McRee J. The activities of coenzyme Q10
and vitamin B6 for immune responses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
1993;193(1):88-92
[12] Durga J, Verhoef P, Anteunis LJ, Schouten E, Kok FJ. Effects
of folic acid supplementation on hearing in older adults: a randomized,
controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146(1):1-9
[13] Sierpina VS, Wollschlaeger B, Blumenthal M. Ginkgo biloba. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68(5):923-926
[14] Meyer B. Multicenter randomized double-blind drug vs. placebo
study of the treatment of tinnitus with Ginkgo biloba extract [in
French]. Presse Med 1986;15:1562-4, cited in Sierpina, et al
[15] Thiel R., Fowkes S.W. Down syndrome and thyroid dysfunction:
Should nutritional support be the first-line treatment? E-pub
March, 2007
[16] Duan M, Qiu J, Laurell G, Olofsson A, Counter SA, Borg E.
Dose and time-dependent protection of the antioxidant
N-L-acetylcysteine against impulse noise trauma. Hear Res. 2004
Jun;192(1-2):1-9
[17] Rice bran, crude. USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 17, 2004
[18] Versendaal D.A., Versendaal-Hoezee D. Contact Reflex Analysis and
Designed Clinical Nutrition. Hozee Marketing, Holland (MI), 1993
[19] Thiel R. Serious Nutrition for Health Care Professionals.
Center for Natural Health Research, Arroyo Grande (CA), 1996
[20] Schaeffer MC. Attenuation of acoustic and tactile startle
responses of vitamin B-6 deficient rats. Physiol Behav. 1987;40(4):473-8
[21] Edamatsu H, Hasegawa M, Oku T, Nigauri T, Kurita N, Watanabe
I. Treatment of sudden deafness: carbon dioxide and oxygen
inhalation and steroids. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1985
Apr;10(2):69-72
[22] Shemesh Z, Attias J, Ornan M, Shapira N, Shahar A. Vitamin
B12 deficiency in patients with chronic-tinnitus and noise-induced
hearing loss. Am J Otolaryngol. 1993;14(2):94-99
[23] Gok U, Halifeoglu I, Yildiz M. The levels of vitamins A, E,
B12 and folic acid in noise-induced hearing loss. Kulak Burun
Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2004;12(3-4):60-64
[24] Quaranta A, Scaringi A, Bartoli R, Margarito MA, Quaranta N.
The effects of 'supra-physiological' vitamin B12 administration on
temporary threshold shift. Int J Audiol. 2004 Mar;43(3):162-165
[25] Shambaugh GE Jr. Zinc: the neglected nutrient. Am J Otol. 1989 Mar;10(2):156-160
[26] Gunther T, Rebentisch E, Vormann J. Protection against
salicylate ototoxicity by zinc. J Trace Elem Electrolytes Health
Dis. 1989;3(1):51-53
[27] Arda HN, Tuncel U, Akdogan O, Ozluoglu LN. The role of zinc
in the treatment of tinnitus. Otol Neurotol. 2003;24(1):86-89
[28] Ochi K, Kinoshita H, Kenmochi M, Nishino H, Ohashi T. Zinc
deficiency and tinnitus. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2003;30 Suppl:S25-28
Some of these studies (or citations) may not conform to peer review standards, therefore, the results are not conclusive. Professionals can, and often do, come to different conclusions when reviewing scientific data. None of these statements have been reviewed by the FDA. All products distributed by Doctors’ Research, Inc. are nutritional and are not intended for the treatment or prevention of any medical condition.
 |
||
|
||
