
C Complex
60 Tablets $27.98 180 Tablets $72.98
180 Tablets $72.98
60 Tablets $27.98
Unlike regular ‘natural’ ascorbic acid or mineral ascorbate supplements, Food C Complex is a concentrated food and contains the bioflavonoids, amino acids, fiber, and other constituents of vitamin C rich foods. Structural differences between Food C Complex and so-called ‘natural’ ascorbic acid can be seen in these light microscope pictures:
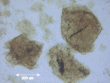 |
 |
| Food Vitamin C | Regular 'Natural' Ascorbic Acid |
Food C Complex is NOT the Same, Food C Complex is MUCH Better! Those astonishing pictures above tell only part of the story. Unlike some ascorbic acid supplements which have some food added to them, Food C Complex is a Food.
Vitamin C in Foods exists in at least two distinguishable forms with accompanying Food factors [1]. Yet, regular ascorbic acid as well as mineral ascorbates are too incomplete to be properly called vitamin C as they do not contain both forms nor the accompanying Food factors [1]! It is of interest to note that even Albert Szent Gyorgyi, while accepting the Nobel prize for isolating ascorbic acid, told scientists that isolated ascorbic acid did not work by itself--it worked best with the factors that are naturally found with it in foods such as citrus (Food C Complex is a citrus Food!). Citruscontains both natural forms of vitamin C [1].
Ascorbic acid is made by fermenting refined sugar into sorbitol, then hydrogenating it until it turns into sorbose, then acetone (commonly referred to as nail polish remover) is added to break the molecular bonds which creates ascorbic acid!How ‘natural’ is that? Food C Complex is a food, regular ‘natural’ ascorbic acid is not.
It has been correctly written that “it was not honest to use the term ‘vitamin C’ for ascorbic acid. That term ‘should be reserved for the vitamin C COMPLEX’. As recently as 1993, to differentiate articles sold as drugs from nutritional supplements, the US Pharmacopeia referred to ‘ascorbic acid’ as a recognized drug name and ‘vitamin C’ as a recognized food name” [2]. That is a good way even today to think of the difference: Food C Complex is a biologically-produced Food, while regular ‘natural’ ascorbic acid is pharmaceutically manufactured.
An in vitro study found that Food C Complex has negative ORP (oxidative reductive potential) [3], yet the Merck Index shows that so-called ‘natural’ ascorbic acid has positive ORP [4] (negative ORP is much better as it helps ‘clean up’ oxidative damage whereas items with positive ORP do not) [5]. Food C Complex is also 10x less acidic than ascorbic acid.
One study found that Food C Complex had proven to have 492 micro moles per gram T.E. (Trolox equivalents) of hydrophilic ORAC (oxygen radical absorbance capacity) [6]—ORAC is essentially a measurement of the ability to quench free radicals (antioxidant ability)—while blueberries (one of the highest ORAC sources [7]) only had 195 micro moles per gram T.E. [6]—thus Food C Complex has 2.52 times the ORAC ability of blueberries. Vitamin C containing food has over 15.6 times the ORAC of isolated ascorbic acid [7] (Food C Complex may be infinitely higher). Actually, there are doubts that isolated ascorbic acid has any significant antioxidant effects in humans [8]. Food C Complex is clearly superior for any interested in ORAC—which should include everyone!
Although “the bioavailability of vitamin C in humans and...our current understanding of that process and factors that influence it are incomplete” [9], it appears that slower disintegration times improve the bioavailability of vitamin C [10] (Food C Complex has slower disintegration times). Some of the many functions that vitamin C is involved in include collagen formation, carnitine biosynthesis, neurotransmitter synthesis, enhancement of iron absorption, immunocompetence, antioxidant defense, possible anticarcenogenic effects, protection of folate and vitamin E from oxidation, and cholesterol catabolism [1].
Why 400 mg? Research from the National Academy of Sciences suggests that the maximum vitamin C benefits (presuming healthy people in a healthy environment) come from consuming 400 mg of vitamin C per day [11]. “Plasma is completely saturated in doses of 400 mg and higher daily producing a steady-state plasma concentration of 80 mM” [8]. That does not mean that some do not benefit from higher amounts, but only that this is an excellent amount for those looking for a reasonably high benefit level.
Bioflavonoids are flavonoids which are found in plants and animals which possess antioxidant actions against “free radicals” and have vitamin-like activity [12]. “Flavonoids are natural substances which have antioxidant activity. Flavonoids are scavengers of superoxide anion and lipid peroxyl radicals and can sequester metal ions through liganding...flavonoids inhibit in vitro oxidation and cytoxicity of LDL. Flavonoids can inhibit cyclo-oxygenase activity and therefore reduce platelet aggression and thrombosis” [13]. Food C Complex bioflavonoids contain as many as sixteen truly organic bioflavonoids: flavanone glycosides, naringin, neorioctrin, neohesperidin, hesperiden, flavone glycosides, rhoifolin, luteolin, neodiosnin, flavon aglycones, tetra-o-methylisoscutellaren, sinensetin, isosinensetin, tangeritin, nobiletin, 5-0-desmethylnobiletin--other bioflavonoid-containing formulas typically are less complete.
Fiber: Each C Complex contains 104 mg of soluble and insoluble fiber. Both fibers are important for human health. Few women meet the National Cancer Institute recommendations for consuming 20g of fiber per day [14]. Dietary fiber helps regulate nutrient absorption, sterol metabolism, cecal fermentation, and stool weight [15]. Shortages may lead to cholesterol problems, certain cancers, digestive problems, cardiovascular concerns, and nutrient problems [14,15].
You and your clients should take Food C Complex daily because vitamin C, “can readily donate electrons to quench a variety of reactive free radical and oxidative species and is easily returned to its reduced state...The vitamin efficiently scavenges hydroxyl, peroxyl, and superoxide radicals, as well as reactive peroxide, singlet oxygen, and hypochlorite species” and protects against lipid and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) peroxidation” [1]. “Vitamin C has antioxidant activity. It may also have anti-atherogenic, anticarcinogenic, antihypertensive, antiviral, antihistaminic, immunomodulatory, opthalmoprotective and airway-protective actions. Vitamin C may aid in the detoxification of some heavy metals, such as lead and other toxic chemicals. Vitamin C is arguably the most important water-soluble biological antioxidant. It can scavenge both reactive oxygen species and nitrogen reactive species” [16]. Food C Complex is a superior Food and the truly Food choice for complete vitamin C supplementation!

Contains naturally occurring carbohydrates, lipids, proteins (including all ten essential amino acids), and truly organic bioflavonoids as found in the edible portions of citrus fruits with mixed plant fiber Cellula vegetabalis --all the nutrients shown above are contained in these foods. Unlike many so-called “natural” formulas containing vitamin C, C Complex is a food complex which contains no isolated USP ascorbic acid, but only contains foods, food complexes, and food concentrates.
Numerous
university studies have concluded that supplements containing food
nutrients are better than USP isolates. Food nutrients are better
because they contain important enzymes, peptides, and phytonutrients
CRITICAL to the UTILIZATION of vitamins and minerals which are not
present in isolated USP nutrients. Published research has concluded
that food vitamins are superior synthetic/USP vitamins.
Suggested use: 1-3 tablets per day or as recommended by your health
care professional. Adjust usage according to nutritional lifestyle
requirements.
References
[1] Turner G. Spectral Data Services. Tests conducted Feb. 1993
[2] DeCava JA. The Lee Philosophy -- Part II. Nutrition News and Views 2003; 7(1):1-6
[3] Thiel R. ORP Study on Durham-produced Food Vitamin C for Food Research LLC. Doctors’ Research Inc., Arroyo Grande (CA), February 17, 2006
[4] Budavari S ed. The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals, 12 th ed. Merck & Co, Whitehouse Station (NJ), 1997
[5] Thiel RJ. The truth about vitamins in supplements. ANMA Monitor, 2003;6(2):6-14
[6] ORAC Test by Brunswick Laboratories, Wareham (MA), February 2006
[7] Williams D. ORAC values for fruits and vegetables. Alternatives, 1999;7(22):171
[8] Sebastian J, et al. Vitamin C as an antioxidant: evaluation of its role in disease prevention. J Am Coll Nutr, 2003;22(1):18-35
[9] Mayersohn M. Vitamin C bioavailability. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol,1992;Spec:446-449
[10] Bhagavan HN, Wolkoff BI. Correlation between the disintegration time and the bioavailability of vitamin C tablets. Pharm Res,1993;10(2):239-242
[11] Levine M, Conry-Cantilena C, Wang Y, Welch RW, Washko PW, Dhariwal KR, Park JB, Lazarev A, Graumlich JF, King J, Cantilena LR. Vitamin C pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers: evidence for a recommended dietary allowance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 16;93(8):3704-3709
[12] Ensminger AH, Ensminger ME, Konlade JE, Robson JRK. Food & Nutrition Encyclopedia, 2nd ed. CRC Press, New York, 1993
[13] Catapano AL. Antioxidant effect of flavonoids. Angiology,1997;48(1):39-44
[14] Thompson FE, et al. Sources of fiber and fat in the diets of U.S. women ages 19 to 50: implications for nutritional education and policy. Am J Pub Health 1992, 82(5):695-702
[15] Dietary fiber: importance of function as well as amount. Lancet 1992, 340:1133-1134
[16] Hendler SS, Rorvik D, editors. PDR for Nutritional Supplements. Medical Economics, Montvale (NJ), 2001
Some of these studies (or citations) may not conform to peer review standards, therefore, the results are not conclusive. Professionals can, and often do, come to different conclusions when reviewing scientific data. None of these statements have been reviewed by the FDA. All products distributed by Doctors’ Research, Inc. are nutritional and are not intended for the treatment or prevention of any medical condition.
 |
||
|
||
