
60 Tablets $23.98
Vegetarian Formula * Dietary Supplement
 |
||
|
||
Doctors who study calcium understand that “The amount of calcium absorbed depends on its interaction with other dietary constituents...The absorbability of calcium is mainly determined by the presence of food constituents” [1]. One study found that calcium from bone meal/powder is only absorbed 1.13 times more than calcium carbonate [2]). It appears that cultures that obtain their calcium from plant sources have the lowest incidence of osteoporosis. Research has shown in groups of people who consume 300 mgs of Food calcium per day or less from plant sources that they have low incidences of osteoporosis [3,4] (100% Food Calcium Complex is a plant source of calcium).
Calcium is found in Food with accompanying Food factors including protein chaperones which aid in absorption of calcium (calcium mineral salts are chemical compounds which are industrially processed rocks). When serum calcium levels drop, calcium leaves the bone, therefore higher absorption of calcium is better for bone health [1]. Clinical reports consistently confirm that dietary/food calciums [5-8] are important in the management of blood pressure. This does not appear to be the case with isolated calcium salts (the results appear inconsistent [5-8]). One study found that calcium in Food raised serum ionic calcium levels from 1.08 to 1.15 mmoles, but that serum ionic calcium levels were not raised with calcium carbonate [6]. Serum calcium levels affect blood pressure [5,9]. Since low bone mass is somewhat inversely correlated with high levels of diastolic blood pressure [9], this suggests that calcium from Food may be superior when hypertension issues are present. Calcium is important for optimal health as calcium deficiencies can contribute to osteoporosis, muscle (especially the legs) cramps, insomnia, mood/behavioral/nerve problems, hypertension, kidney stones, and colon cancer [1,4,5].
Plants convert soil constituents including calcium into Food [10]. Humans are supposed to consume Food, not soil [10]. Yet most calcium-containing supplements do not contain calcium as found in Foods ; instead they contain various acid-processed rocks or other mineral salts. Consuming mineral salts poses at least two problems. The first is that the body has to attempt to breakdown the rock into its elemental (ionic) forms, which it is not really designed to do (plants are supposed to do that [10], which is why they are considered to be lower down on the food chain than humans). The second is that the body has to discard the non-calcium portion somehow as it may not be of any use to the body (if undesirable elements accumulate, they can contribute to toxic accumulations and/or reactions in the body, including free radicals). Because it is a Food and not ground up rock, 100% Food Calcium Complex is much easier on the digestive system than other calcium supplements and can often be better tolerated by sensitive individuals.
What Kind of Calcium is in Your Calcium Supplements?
| Calcium Form | Actually Is/ Often Used As |
| Calcium Carbonate | The rock known as limestone/ used to make paint, rubber, chalk, etc. [11]. |
| Calcium Citrate | Limestone processed w/ lactic & citric acids/ used to change properties of flour [11]. |
| Calcium Gluconate | Limestone processed with gluconic acid/ used in sewage purification [11]. |
| Calcium Hydroxy-Appetite | Processed bone meal high in bone marrow/ used in some animal products. |
| Calcium Lactate | Limestone processed with lactic acid / used as a preservative [11]. |
Food Calcium Enzymatically processed plants/ only used as a food.
Calcium mineral salts are primarily industrial products--they are not natural foods intended for human consumption! Calcium carbonate (also called chalk) and calcium citrate have a very alkaline pH and can be used as an antacid (which makes them a compromised choice for calcium supplementation since calcium carbonate and calcium citrate need an acidic environment [1] in order to be ionized into a usable form). Calcium carbonate’s main uses are in the manufacture of paint, rubber, plastics, paper, dentrifices, and ceramics [11]. One of the main uses of calcium citrate is changing the baking properties of flour [11]. The main uses of calcium gluconate appear to be to prevent caking in coffee powders and to purify sewage [11]. The main use of calcium lactate appears to be as a preservative [11].
Since humans do not absorb minerals in rock form such as plants do (this is one of the ways that plants and humans differ), should we swallow rocks processed with various acids for calcium, eat processed bones, or consume natural calcium as found in plants? Humans do not naturally eat rocks, egg shells, oyster shells, or coral (all of which contain calcium in the alkaline mineral salt form known as calcium carbonate; it should be noted that calcium needs an acidic, not alkaline environment for absorption [1]), so why would anyone wish to swallow them for long-term calcium needs?
Interestingly in 1999, the Nobel prize in medicine was awarded for the finding that humans need protein chaperones in order for minerals to be absorbed into the cell. Calcium mineral salts do not contain protein chaperones, yet 100% Food Calcium Complex naturally contains protein chaperones such as ceruloplasmin and ATX1 [12,13]. 100% Food Calcium Complex also naturally contains minerals such as phosphorus and magnesium which are needed for proper calcium absorption [1], plus potassium which is one of the body’s most important electrolytes [1].
Some calcium supplements claim to be ‘amino acid chelates’. While these chelates generally are more recognizable to the body than calcium mineral salts, they are not natural Food. Calcium chelates are normally the result of synthesized amino-acids chemically combined with a rock-derived element (limestone or oyster shell)--they are not Food!
100% Food Calcium Complex naturally contains superoxide dismutase (S.O.D.). S.O.D. “is one of the most important enzymes that functions as a cellular antioxidant...The absence of this enzyme is lethal” [1]. Studies show that S.O.D. is helpful for heart, lungs, joints, kidneys, liver, muscles, and skin [14]. 100% Food Calcium Complex also contains a minimum of 255 mg of soluble and insoluble rice bran and vegetable fiber per serving. Dietary fiber helps regulate nutrient absorption, sterol metabolism, cecal fermentation, and stool weight [15]. Shortages may lead to cholesterol problems, certain cancers, digestive problems, cardiovascular concerns, and nutrient problems [15,16].
Rice bran is also a food complex source of silicon and B vitamins [17,18], while dulse and kelp are excellent Food complex source of trace minerals [19]--all are found in 100% Food Calcium Complex. Silicon and trace minerals are essential for strong and healthy bones (as well as skin, nails, and hair) [17].
Food researchers have concluded that 100% Food Calcium Complex is “the most suitable form of calcium for long-term supplementation” [2]. It does not cause stomach upset as nightly alkaline calcium rock forms do. 100%Food Calcium Complex is the right choice for calcium supplementation [2].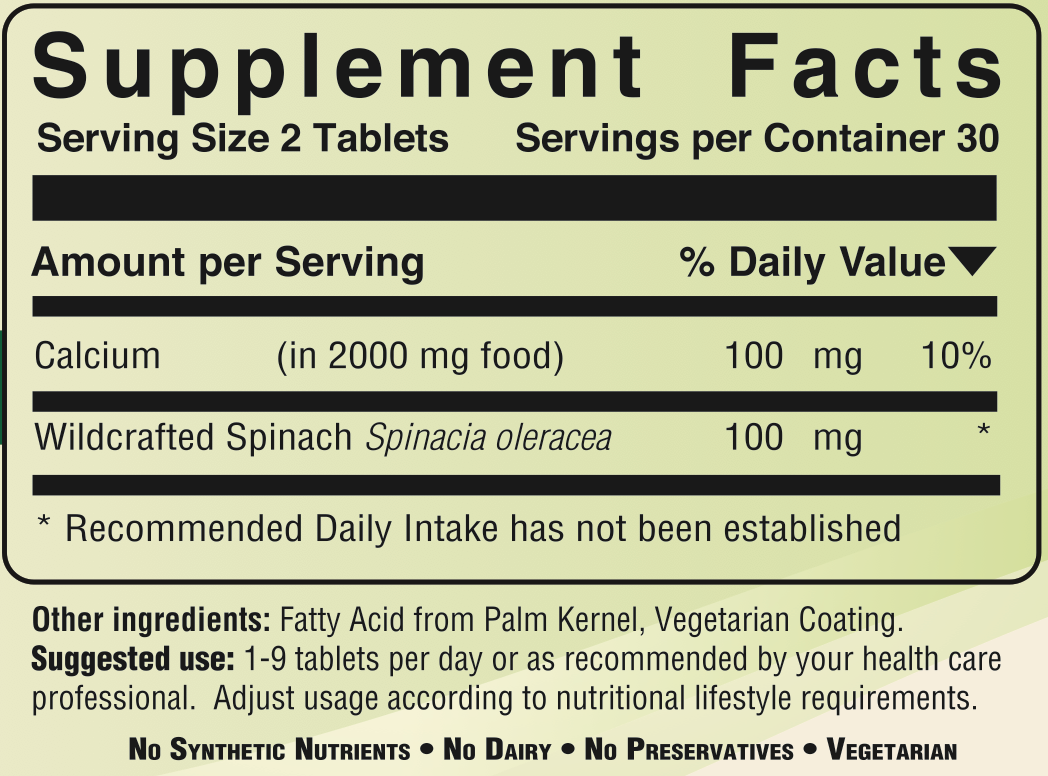
Contains
naturally occurring carbohydrates, lipids, proteins (including all ten
essential amino acids), superoxide dismutase, and truly organic
bioflavonoids as found in enzymatically processed Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Rice bran Oryza sativa, Mixed vegetable fiber Cellula vegetabalis, Kelp thallus Ascophyllum nodesum, Dulse plant Rhodymenia palmatta, and Buckwheat rutin Fagopyrum esculentum --all the nutrients shown above are contained in these foods. Unlike many so-called “natural” calcium formulas, Calcium Complex
is a true food calcium (not a mineral salt) contains no synthetic USP
nutrients or mineral salts, but only contains foods, food complexes,
and food concentrates.
Numerous
university studies have concluded that supplements containing food
nutrients are better than USP isolates. Food nutrients are better
because they contain important enzymes, peptides, and phytonutrients
CRITICAL to the UTILIZATION of vitamins and minerals which are not
present in isolated USP nutrients. Published research has concluded
that food vitamins are superior synthetic/USP vitamins.
Suggested use: 1-9 tablets per day or as recommended by your health
care professional. Adjust usage according to nutritional lifestyle
requirements.
 Calcium Complex Video
Calcium Complex Video
References
[1] Shils ME, Olson JA, Shike M. Calcium and Phosphorus. In Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 8th ed. Lea & Febiger, Phil; 1994:144-163
[2] Heaney RB. Calcium in the prevention of osteoporosis. J Int Med, 1992;231:169-180
[3] Spindler A. Bone mineral density in a native population of Argentina with low calcium intake. J Rheumatol, 1995;22(11):2148-2151
[4] Knight KB, Keith RE. Effects of oral calcium supplementation via calcium carbonate versus diet on blood pressure and serum calcium in young, normotensive adults. J Opt Nutr, 1994;3(4):152-158
[5] Orlov SN, Li JM, Tremblay J, Hamet P. Genes of intracellular calcium metabolism and blood pressure control in primary hypertension. Semin Nephrol. 1995 Nov;15(6):569-592
[6] Hamet P, et al. The evaluation of the scientific evidence for a relationship between calcium and hypertension. J Nutr, 1995;125:311S-400S
[7] Osborne G, et al. Evidence for the relationship of calcium to blood pressure. Nutr Reviews, 1996;54(12):365-381
[8] Yamamoto ME., et al. Lack of blood pressure effect with calcium and magnesium supplementation with adults with high-normal blood pressure results from phase I of the Trials of Hypertension and Prevention (TOHP). Ann Epidem, 1995;5:96-107
[9] Afghani A, Johnson CA. Resting blood pressure and bone mineral content are inversely related in overweight and obese Hispanic women. Am J Hypertens. 2006;19(3):286-292
[10] Cronquist A. Plantae. In Synopsis and Classification of Living Organisms, Vol. 1. McGraw-Hill, 1982:57
[11] Budavari S, et al. The Merck Index, 12th ed. Merck & Co., Whitehouse Station (NJ), 1996
[12] Rouhi AM. Escorting metal ions: protein chaperone protects, guides, copper ions in transit. Chem Eng News, 1999;11:34-35
[13] Himelblau E, et al. Identification of a functional homolog of the yeast copper homeostasis gene ATX1 from Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 1998;117(4):1227-1234
[14] Null G. The Clinician’s Handbook of Natural Healing, Kensington, NY, 1998
[15] Thompson FE, et al. Sources of fiber and fat in the diets of U.S. women ages 19 to 50: implications for nutritional education and policy. Am J Pub Health 1992, 82(5):695-702
[16] Dietary fiber: importance of function as well as amount. Lancet 1992, 340:1133-1134
[17] Nielsen FH. Ultratrace minerals. In Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 9th ed. Williams and Wilkins, Balt.;1999:283-303
[18] Jensen B. The Chemistry of Man. Bernard Jensen, Escondido, 1983
[19] Seaweed, kelp, raw. USDA Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 11-1, August 1997
Some of these studies (or citations) may not conform to peer review standards, therefore, the results are not conclusive. Professionals can, and often do, come to different conclusions when reviewing scientific data. None of these statements have been reviewed by the FDA. All products distributed by Doctors’ Research, Inc. are nutritional and are not intended for the treatment or prevention of any medical condition.